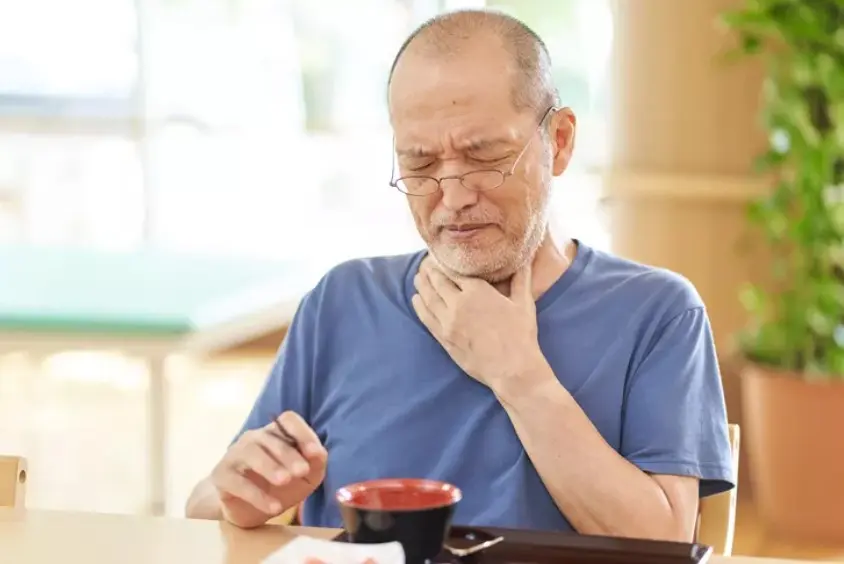
Eating is one of the most basic human needs, yet for some people, it can be a daily struggle. Difficulty eating — whether it’s pain while chewing, trouble swallowing, or loss of appetite — can severely impact nutrition, health, and quality of life. Understanding why eating becomes hard is the first step toward finding relief and improving overall well-being. In this post, we’ll explore some of the most common causes of difficulty eating and what you can do about them.
What Does “Difficulty Eating” Mean?
Difficulty eating is a broad term that can refer to any problem that makes the act of consuming food challenging. This can include:
- Pain while chewing or swallowing
- Feeling like food is stuck in the throat or chest
- Trouble moving food around the mouth
- Loss of appetite or early fullness
- Nausea or vomiting during or after meals
The causes can range from simple dental issues to complex medical conditions affecting nerves or muscles. Let’s dive into some common reasons why eating might become hard.
1. Dental Problems
One of the most straightforward reasons for difficulty eating is poor oral health. Dental pain, cavities, gum disease, or missing teeth can make chewing uncomfortable or even painful. Conditions like tooth decay and periodontal disease can cause inflammation and sensitivity, discouraging you from eating properly. Additionally, ill-fitting dentures or dental appliances may also interfere with your ability to chew or bite down effectively.
What to Do
Maintaining regular dental checkups and practicing good oral hygiene are essential. If you experience ongoing pain or discomfort, it’s important to visit a dentist without delay. Early treatment of cavities or gum problems can help prevent them from getting worse. If you’re in the High Point, NC area, consider consulting with a local specialist for dentures or other dental solutions to improve your eating comfort.
2. Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia)
Dysphagia is the medical term for difficulty swallowing. This can happen for various reasons, including neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, or muscle problems. People with dysphagia may feel like food gets stuck in the throat or chest, cough or choke while eating, or experience pain.
Common causes of dysphagia include:
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Esophageal strictures or narrowing
- GERD (acid reflux causing damage to the esophagus)
What to Do
If swallowing difficulties persist, it’s important to seek medical evaluation. A speech-language pathologist or gastroenterologist can perform tests and recommend treatments such as swallowing therapy or dietary modifications.
3. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Saliva plays a vital role in digestion by helping to moisten food, making it easier to chew and swallow. Dry mouth, or xerostomia, can make eating uncomfortable and difficult. It’s often caused by medications, dehydration, or certain medical conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome.
What to Do
Drinking plenty of water, using saliva substitutes, and avoiding caffeine or alcohol (which can dry out the mouth) can help. If medication is the cause, talk to your doctor about possible alternatives.
4. Gastrointestinal Issues
Several digestive tract problems can lead to eating difficulties. For example, acid reflux disease (GERD) can cause pain or discomfort after eating. Esophageal spasms or strictures can physically block food passage. Additionally, conditions like gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying) can cause early fullness, nausea, and vomiting.
What to Do
If you experience pain or discomfort during or after meals, a gastroenterologist can help diagnose the problem and provide treatment, which may include medications, dietary changes, or in some cases, procedures.
5. Neurological and Muscular Disorders
Eating involves complex coordination between the brain, nerves, and muscles. Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, ALS, or stroke can disrupt this coordination, leading to problems with chewing and swallowing.
What to Do
Managing the underlying neurological condition and working with therapists trained in swallowing and feeding techniques can improve safety and ease of eating.
6. Psychological Causes
Sometimes, difficulty eating can stem from psychological issues such as anxiety, depression, or eating disorders like anorexia or bulimia. These conditions can reduce appetite, cause aversion to food, or disrupt normal eating patterns.
What to Do
Professional mental health support is essential. Nutritional counseling and therapy can help rebuild a healthy relationship with food.
7. Infections and Inflammation
Oral infections such as thrush (oral candidiasis), or inflammatory conditions like tonsillitis or pharyngitis, can cause pain and swelling that make eating uncomfortable. Similarly, inflammatory diseases affecting the esophagus or stomach lining can cause eating difficulties.
What to Do
Treatment usually involves medications such as antifungals, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drugs, depending on the cause.
When to See a Doctor
Difficulty eating should never be ignored, especially if accompanied by:
- Significant weight loss
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Choking or coughing while eating
- Signs of dehydration or malnutrition
- Difficulty swallowing liquids as well as solids
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Eating should be a pleasurable and nourishing part of life. When it becomes hard, it signals an underlying issue that needs attention. Whether it’s a dental problem, a swallowing disorder, or something else entirely, understanding the root causes can guide you toward the right care. If you or a loved one is experiencing difficulty eating, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice to regain comfort and confidence at mealtime.
Also Read-Ztec100.com Tech Health And Insurance