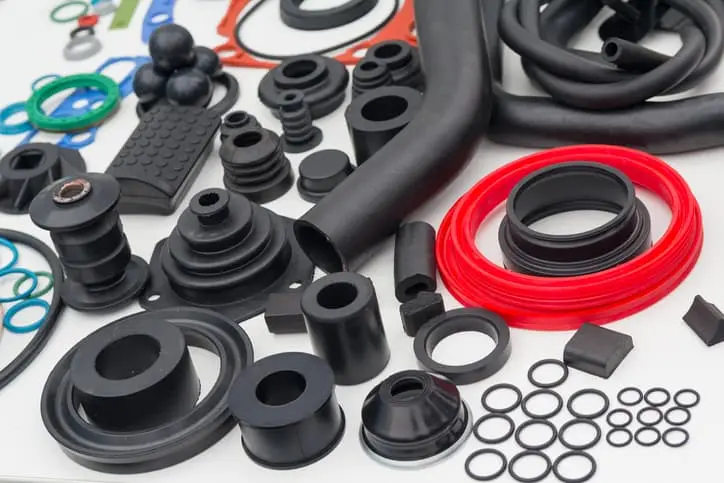
Insert molding has become an essential technique in manufacturing, combining the elasticity of rubber with the durability of other materials like metal or plastic. This process delivers a powerful solution for producing components that need both flexibility and strength, helping industries meet high-performance and design standards. It serves as a practical and adaptable approach to meet the needs of sectors where reliability, efficiency, and material integration are key factors.
Understanding the Insert Molding Process
Rubber insert molding involves placing a solid insert, typically made from metal or plastic, into a mold. Rubber is then injected into the mold cavity, where it encapsulates or bonds to the insert. As the rubber cures, it forms a single part that combines the benefits of both materials. The result is a durable product that maintains the flexibility of rubber along with the strength and rigidity of the insert.
This method is especially useful when parts must absorb shock, resist wear, or withstand chemical exposure while remaining lightweight and functional. The seamless bond created during the molding process ensures long-term performance, reducing the chance of failure that might occur with mechanical fastening or adhesive bonding. Because the rubber adheres tightly to the insert, it prevents delamination or movement during use, enhancing the integrity of the final part.
Insert molding also allows for better alignment and precision in complex assemblies. Since the insert is placed and held securely during the molding process, the final part comes out with tight tolerances and consistent quality. This is crucial for components that need to fit into assemblies with little room for variation.
Key Benefits for Industrial Use
One of the most attractive features of insert molding is its ability to reduce or eliminate secondary assembly operations. Since the rubber is molded directly over or around the insert, there is no need to glue or fasten separate components together. This simplifies production lines, lowers labor costs, and increases output. Reducing post-molding processes also minimizes the risk of assembly errors and inconsistencies.
Another major benefit lies in its durability. Molded parts can better handle vibration, temperature changes, and environmental exposure. This increases the component’s life span and reliability, which is critical in applications such as engine mounts, medical devices, and vibration isolators. The consistent bond between rubber and insert provides long-term stability under mechanical stress and environmental fluctuations.
Also, the process enables complex designs that are difficult or even impossible to achieve with traditional molding or assembly methods. Insert molding offers design freedom, especially valuable in applications with space constraints or performance-critical geometries. Engineers can integrate multiple functions into a single molded component, reducing part count and assembly complexity.
Material Compatibility and Performance
The success of insert molding depends on material selection. Common rubber types include silicone, EPDM, nitrile, and natural rubber. Each has its strengths, whether it be resistance to heat, oil, chemicals, or weathering.
The insert material must match the rubber in performance and bonding. Common choices include stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and high-strength plastics, selected for support, corrosion resistance, or conductivity. When selected carefully, the material pairings deliver consistent performance under mechanical stress, temperature swings, and exposure to harsh environments.
Common Applications Across Sectors
Insert molding serves many industries due to its versatility. In automotive manufacturing and the machinery and equipment industry, it’s used for gaskets, mounts, and seals that demand both strength and flexibility. These parts must absorb engine vibrations while holding up under extreme temperatures.
In medical equipment, molded inserts ensure hygienic, flexible parts that securely bond with rigid components, supporting safety and function. Consumer electronics use the process for durable buttons, grips, and connectors that blend softness with structural support. Industrial equipment benefits from vibration-resistant mounts and connectors produced through insert molding.
Support for Complex Manufacturing Needs
Insert molding provides a valuable solution for projects requiring a fusion of flexibility and strength. As production demands grow more complex, manufacturers need methods that balance durability with streamlined assembly. This molding technique supports high-volume runs without sacrificing part performance, design intricacy, or long-term reliability, making it ideal for both standard and custom-engineered applications across various industries.
It also provides advantages in terms of cost savings over the product life cycle. Fewer assembly steps mean fewer potential points of failure, and the ability to integrate multiple components into a single molded part reduces the need for additional hardware or labor. These efficiencies help meet tight production deadlines and budget constraints while maintaining quality standards.
Insert molding stands out as a dependable and efficient solution in modern manufacturing, enabling the production of high-performance components that combine strength, flexibility, and precision. Its adaptability across materials and industries, along with its ability to streamline production and improve part longevity, makes it a valuable asset for meeting current and future manufacturing demands. Rubber insert molding plays a key role in achieving secure material bonds and consistent quality across complex assemblies. As technology and product complexity continue to evolve, this method remains a practical approach for achieving durable, cost-effective, and highly functional components.
Also Read-V4Holt: Leading Advances in Innovative Tech