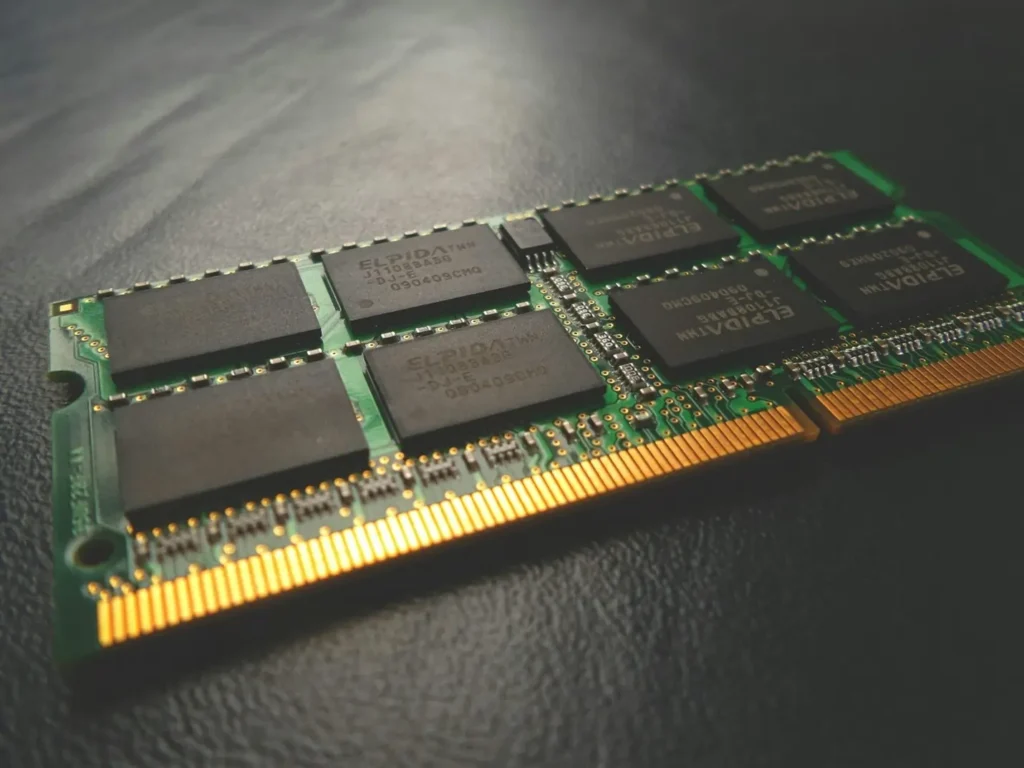
As embedded systems evolve to meet the demands of modern applications, the balance between data processing speed and energy efficiency becomes critical. Traditionally, data storage and computation happen in separate locations, often causing performance delays and excessive power consumption due to the physical distance between memory and processing units. Near-memory storage technology offers a compelling solution by moving memory closer to compute units. This proximity significantly reduces latency, boosts bandwidth, and enhances system responsiveness. It has the potential to transform how embedded systems handle massive data, especially in real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and industrial automation.
1. The Bottleneck of Traditional Memory Architecture
Most embedded systems rely on conventional architectures where data frequently travels between the central processing unit (CPU) and memory. This model suffers from what engineers call the “memory wall,” a bottleneck where the speed of memory access lags far behind processing speeds. As embedded systems become more intelligent and data-hungry, this latency costs time and energy. Data must often traverse through multiple cache layers or external buses, leading to inefficient power use. With space and energy constraints common in embedded devices, closing this gap becomes vital to optimizing both performance and battery life.
2. What Is Near-Memory Storage and How It Works
Near-memory storage places memory modules in immediate proximity to processing cores, either within the same chip package or on the same die. Unlike traditional architectures, this design shortens the physical pathway data must travel, reducing latency and improving bandwidth. The result is a more seamless, high-speed interaction between memory and compute resources. By processing data where it resides, near-memory systems avoid frequent trips across buses, slashing both energy consumption and operational delays. Companies like https://lexarenterprise.com/ are pioneering advanced memory solutions tailored for high-efficiency embedded environments, providing the kind of speed and durability that support next-generation processing requirements.
3. Advantages of Near-Memory Storage for Embedded Systems
Near-memory storage offers substantial advantages that align perfectly with the goals of embedded system designers. First, it improves data throughput, which is crucial for real-time applications that require swift decision-making, like robotics or automotive controls. Second, it reduces power consumption because the system avoids energy-intensive data shuttling across long buses. Third, it allows for a smaller footprint, which is essential in embedded designs where space is limited. These benefits create a powerful synergy between speed, energy efficiency, and compact design, making near-memory storage a game-changer for developers focused on edge computing and AI-driven tasks.
4. Use Cases Across Critical Industries
The impact of near-memory storage spans multiple industries that rely on embedded systems. In healthcare, it enables faster processing of patient data from wearable monitors. In automotive systems, it supports advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) by accelerating the analysis of sensor inputs. Industrial automation benefits from quicker machine response times, increasing productivity and safety. Even in consumer electronics, such as smart home devices, this architecture improves responsiveness while extending battery life. These use cases prove that the proximity of memory to compute isn’t just a theoretical advantage; it delivers tangible improvements across real-world applications where every millisecond counts.
5. How Near-Memory Storage Supports AI at the Edge
AI applications at the edge require rapid data processing without depending on cloud infrastructure. Near-memory storage provides the ideal foundation for this, allowing AI models to analyze data locally in near real-time. This reduces the need for network connectivity, enabling systems to function reliably even in remote or mobile environments. For instance, surveillance cameras with embedded AI can detect anomalies instantly without uploading data to a central server. Similarly, drones analyzing terrain in-flight benefit from the ultra-low latency made possible by near-memory designs. This architecture empowers smarter, more autonomous behavior at the very edge of computing.
6. Challenges in Implementing Near-Memory Storage
Although near-memory storage offers clear advantages, implementing it in embedded systems introduces several challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is heat dissipation. Placing memory close to processing cores concentrates heat in a small area, which can affect system stability. Engineers must design effective cooling solutions that don’t increase device size. Another concern is compatibility with existing architectures. Many legacy systems were not built to support near-memory configurations, making integration complex. Additionally, cost can be a factor—advanced packaging and 3D stacking technologies often come at a premium. These challenges require careful engineering and thoughtful trade-offs to fully unlock the potential of near-memory storage.
7. Hardware Innovations Driving Adoption
Innovations in chip design and semiconductor packaging have made near-memory storage more accessible than ever. Techniques like 2.5D and 3D stacking allow memory to sit directly on top of or next to logic units, reducing signal travel time. High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) and Embedded Multi-Chip Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) technologies exemplify this trend. These hardware improvements enhance data transfer rates while minimizing power draw. Meanwhile, smaller process nodes—like 5nm and below—enable tighter integration without sacrificing performance. As these technologies mature, they lower the barriers to entry and make it feasible for even mid-tier embedded devices to adopt near-memory architectures efficiently.
8. Software Optimization for Near-Memory Systems
The full benefits of near-memory storage only emerge when software complements the hardware. Developers must optimize code to leverage reduced memory latency and parallel processing capabilities. Memory-aware programming models, such as data locality optimization and parallel thread management, help take advantage of proximity. Additionally, compilers need to support these architectures through intelligent scheduling and cache handling. Real-time operating systems (RTOS) designed for embedded platforms must also be updated to align with near-memory layouts. These software improvements work in tandem with hardware advancements to ensure smooth, efficient, and fast data processing in embedded environments.
Near-memory storage represents a pivotal shift in embedded system design. By reducing the distance between data and compute, it enables faster, more energy-efficient processing—key requirements for modern edge applications. Despite the implementation challenges, ongoing innovations in hardware and software are steadily overcoming barriers. From autonomous vehicles to industrial robots, near-memory architectures are already transforming performance benchmarks. As adoption grows, this approach will no longer be a cutting-edge option but a foundational element in how embedded systems operate. Developers who embrace this change today position themselves to deliver the next wave of powerful, responsive, and efficient smart devices.
What Makes Maltipoo Pups Ideal for Apartment Living
5 Questions to Ask if Tattoo Removal is Right for You